
- Fundamentals of design
- Design of joints, levers and offset links
- Design of shafts, keys and couplings
- Design of power screws
- Design of springs
- Design of bolted and welded joints
- Selection of anti-friction bearings and gears
Fundamentals of machine design
1 During a tensile loading, the length of a steel rod is changed by 2 mm. If the original length of the rod has been 20 mm, what is the amount of strain induced- (A) 0.1
- (B) 2
- (C) 0.9
- (D) 0.22
2 Stress on components is expressed in ….
- (A) N/mm²
- (B) kN/m²
- (C) Pascal
- (D) All of the above
3 Shear forces are —— forces.
- (A) Aligned.
- (B) Unaligned
- (C) Perpendicular
- (D) Parallel
4 The components having length in —— are usually Buckle.
- (A) X- direction
- (B) Y direction
- (C) Z- direction
- (D) X-Y direction
5 Flexure is also known as —–
- (A) Distortion
- (B) Failure
- (C) Bending
- (D) Twisting
6 Cyclic loads below significant load causes
- (A) Bending
- (B) Fatigue
- (C) Wrapping
- (D) Compression
7 Tensile stresses are applied —– to applied tensile force
- (A) Parallel
- (B) Perpendicular
- (C) cross-sectional
- (D) In same direction
8 Compressive forces are
- (A) Towards the point
- (B) Opposite to point
- (C) Both
- (D) Can’t say
9 Strength of material is maximum in
- (A) Tension
- (B) Compression
- (C) Twisting
- (D) Any of above
10 Stressed parts are always kept in tension.
- (A) TRUE
- (B) FALSE
11 While designing a forging, the profile is selected such that the fibrous lines are parallel to the tensile forces and perpendicular to shear forces.
- (A) TRUE
- (B) FALSE
12 Which of the following is not a reason to design and redesign a product?
- (A) Optimum design
- (B) Innovation
- (C) Appearance
- (D) None of the above
13 In design process, which process is followed after selecting the material?
- (A) Selecting factor of safety
- (B) Synthesis
- (C) Analysis of forces
- (D) Determining mode of failure
14 Which of the following is not a reason to design and redesign a product?
- (A) Optimum design
- (B) Innovation
- (C) Appearance
- (D) None of these
15 The following standard(s) is (are) used in Mechanical engineering design.
- (A) Standards for materials
- (B) Standard for testing of products
- (C) Standards for Fits, Tolerances and surface finish of component
- (D) All of the above
16 The following design process is also known as ‘over the wall’ process
- (A) Sequential Design process
- (B) Concurrent Engineering
- (C) Both A and B
- (D) None of the above
17 The elongation of a bar is 0.5 mm, when a tensile stress of 200 N/mm2 acts on it. Determine original length of a bar if modulus of elasticity is 150 x 103.
- (A) 375.93 mm
- (B) 300 mm
- (C) 360 mm
- (D) None of the above
18 Deformation per unit length is called as ________
- (A) strain
- (B) stress
- (C) modulus of elasticity
- (D) none of the above
19 In design process, which process is followed after selecting the material?
- (A) Selecting factor of safety
- (B) Synthesis
- (C) Analysis of forces
- (D) Determining mode of failure.
20 Which of the following materials do not have a well-defined yield point?
- (A) Heat treated steel
- (B) Concrete
- (C) Carbon fiber
- (D) All of the above
21 In stress-strain diagram, up to proportional limit ______
- (A) stress is inversely proportional to strain
- (B) force is directly proportional to displacement
- (C) stress is directly proportional to strain
- (D) strain is directly proportional to stress
22 Factor of safety is the ratio of _________
- (A) working stress and ultimate strength
- (B) yield strength and endurance strength
- (C) ultimate strength and yield strength
- (D) yield strength and working stress
23 The ratio of endurance strength and allowable stress is used to determine FOS for _____
- (A) fatigue loading
- (B) static loading of brittle materials
- (C) static loading of ductile materials
- (D) all of the above
24 Which of the following is the numerator of factor safety formula?
- (A) Working stress
- (B) Shear stress
- (C) Tensile stress
- (D) Ultimate Stress
25 Which of the following can be the factor of safety for a dead load?
- (A) 6
- (B) 2
- (C) 4
- (D) 7
26 Which of the following can be the factor of safety for shock loading?
- (A) 11
- (B) 13
- (C) 4
- (D) 7
27 Factor of safety is used to find out the reliability of the design.
- (A) TRUE
- (B) FALSE
28 What can understand by the factor of safety equal to one?
- (A) It means that the structure will fail under load
- (B) It means that the structure will only support the actual load
- (C) it means that the structure will support more than the actual load
- (D) There is no relation between factor safety and load application
29 For which of the following design factor of safety the design will work properly?
- (A) 0.1
- (B) 1
- (C) 2
- (D) 0.9
30 What is a safe factor of failure for a component which on failure can result in financial loss or serious injury?
- (A) 1
- (B) 2
- (C) 3
- (D) 4
31 Design factor for most aircraft structures is 2.
- (A) TRUE
- (B) FALSE
32 What is the factor of safety under suddenly applied load?
- (A) 2 and 4
- (B) 4 and 8
- (C) 8 and 16
- (D) None
33 Safety factor in case of a ductile material is
- (A) Real stress/unit stress
- (B) Ultimate stress/maximum stress
- (C) Yield stress/ allowable stress
- (D) None
34 Effect of higher factor of safety on cost of the material?
- (A) Increases
- (B) Decreases
- (C) No change
- (D) None
35 The factor of safety for a ductile material
- (A) σyp/σallow
- (B) (b)σult/σallow
- (C) σult/σyp
36 Factor of safety is the ratio of —–
- (A) allowable stress to critical stress
- (B) critical stress to allowable stress
- (C) normal stress to shear stress
- (D) shear stress to normal stress
37 The factor of safety for—–
- (A) steel and concrete are same
- (B) steel is lower than that for concrete
- (C) steel is higher than that for concrete
- (D) none of the above
38 Design is concerned with——
- (A) Selection of material
- (B) Shape and size
- (C) Arrangements of elements
- (D) All of the above.
39 Is analysis of forces important in designing a machine element?
- (A) Yes
- (B) No
- (C) May be
- (D) Can’t say
40 In which of the following step we can change the size of member.
- (A) Detailed drawing
- (B) Modification
- (C) Both A and B
- (D) none of the above
41 Which of the following is not step of machine design?
- (A) Recognition of need
- (B) Mechanism
- (C) Analysis of forces
- (D) Safety of operation
42 To avoid failure which of the following is important.
- (A) Reliability
- (B) Wear resistance
- (C) Strength
- (D) None of the above
43 Need =>Mechanism =>Analysis of forces =>———=> Design of element.
- (A) Modification
- (B) Production
- (C) Quality checking
- (D) Material selection
44 Is quality checking part of machine designing?
- (A) Yes
- (B) No
- (C) May be
- (D) Can’t say
45 To selection of material——.
- (A) Designer should have a deep knowledge about properties of material.
- (B) Knowledge about properties is not important.
- (C) Both A and B can be done.
- (D) None of the above
46 What will happened if standard parts are used?
- (A) Overall cost reduces
- (B) Develops machine work effectively
- (C) Both A and B
- (D) None of the above
47 Which of the following parameters can be obtained by tension test of a standard specimen?
- (A) Proportional limit
- (B) Yield strength
- (C) Percentage reduction in area
- (D) All of the above
48 Yield strength is defined as the maximum stress at which a marked increases in elongation occurs without increases in
- (A) Load
- (B) Strength
- (C) Toughness
- (D) Hardness
49 Which of the following measuring the stiffness?
- (A) Modulus of elasticity
- (B) Modulus of plasticity
- (C) Resilience
- (D) Toughness
50 Modulus of resilience is defined as
- (A) Strain energy per unit volume
- (B) Strain energy per unit area
- (C) Independent of strain energy
- (D) None of the above
51 Malleability increases with temperature while ductility decreases with the temperature
- (A) TRUE
- (B) FALSE
52 Calculate the diameter of pin from shear consideration with maximum shear stress allowed is 40kN/mm² and an axial tensile force of 50kN is acting on the rod.
- (A) 40
- (B) 50
- (C) 60
- (D) 70
53 For an elliptical hole on a flat plate, if width of the hole in direction of the load decrease, Stress Concentration Factor will be
- (A) Increased
- (B) Decreased
- (C) Remains constant
- (D) Can’t be determined. Varies from material to material
54 In which of the following case stress concentration factor is ignored?
- (A) Ductile material under static load
- (B) Ductile material under fluctuating load
- (C) Brittle material under static load
- (D) Brittle material under fluctuating load
55 Use of multiple notches in a V shaped flat plate will be
- (A) Reduce the stress concentration
- (B) Increase the stress concentration
- (C) No effect
- (D) Cannot be determined
56 Which of the following reduces the stress concentration?
- (A) Use of multiple notches
- (B) Drilling additional holes
- (C) Removal of undesired material
- (D) Each of the mentioned
57 Which of the following is measure of stiffness?
- (A) Modulus of elasticity
- (B) Modulus of plasticity
- (C) Resilience
- (D) Toughness
58 irregularities present in the component and no changes of the cross section.
- (A) TRUE
- (B) FALSE
59 Stress Concentration Factor is the ratio of nominal stress obtained by elementary equations for minimum cross-section and highest value of actual stress near discontinuity.
- (A) TRUE
- (B) FALSE
60 If a flat plate with a circular hole is subjected to tensile force, then its theoretical stress concentration factor is?
- (A) 2
- (B) 3
- (C) 4
- (D) 1
61 For an elliptical hole on a flat plate, if width of the hole in direction of the load decrease, Stress Concentration Factor will——
- (A) Increase
- (B) Decrease
- (C) Remains constant
- (D) can’t be determined. Varies from material to material
62 Is it logical to use fluid analogy to understand the phenomenon of stress concentration?
- (A) TRUE
- (B) FALSE
63 Use of multiple notches in a V shaped flat plate will
- (A) Reduce the stress concentration
- (B) Increase the stress concentration
- (C) No effect
- (D) Cannot be determined
64 A flat plate 30mm wide and “t” mm wide is subjected to a tensile force of 5kN. The plate has a circular hole of diameter 15mm with the center coinciding with the diagonal intersection point of the rectangle. If stress concentration factor=2.16, find the thickness of the plate if maximum allowable tensile stress is 80N/mm².
- (A) 8mm
- (B) 9mm
- (C) 10mm
- (D) 12mm
65 The fatigue stress concentration factor is defined as
- (A) The ratio of endurance limit with stress concentration to the endurance limit without stress concentration
- (B) The ratio of endurance limit without stress concentration to the endurance limit with stress concentration
- (C) The product of the endurance limits with and without stress concentration
- (D) All of the above.
66 Stress may be defined as _________
- (A) Force per unit volume
- (B) Force per unit length
- (C) Force per unit area
- (D) None of these
67 The forces acting on the bar as shown in the given figure introduce _________?
- (A) Tensile stress
- (B) Compressive stress
- (C) Shear stress
- (D) None of these
68 The property by which a body returns to its original shape after removal of the force is called __________
- (A) Plasticity
- (B) Elasticity
- (C) Ductility
- (D) Malleability
69 Which law is also called as the elasticity law, which states that stress is proportional to the strain within the elastic limit?
- (A) Bernoulli’s law
- (B) Stress law
- (C) Hooke’s law
- (D) Poisson’s law
70 A member which does not regain its original shape after removal of the load producing deformation is said __________
- (A) Plastic
- (B) Elastic
- (C) Rigid
- (D) None of the mentioned
71 As the elastic limit reaches, tensile strain __________
- (A) Increases more rapidly
- (B) Decreases more rapidly
- (C) Increases in proportion to the stress
- (D) Decreases in proportion to the stress
72 The dimension of strain is?
- (A) LT-2
- (B) N/m2
- (C) N
- (D) Dimensionless
73 Live loads, with time can vary in_________
- (A) Magnitude
- (B) Position
- (C) Neither position nor magnitude
- (D) Position as well as magnitude
74 What is the first step in the ‘General procedure of machine design’?
- (A) Analysis of forces
- (B) Material Selection
- (C) Need or aim
- (D) Detailed drawing
75 Sizes of machine components are decided in which stage of general procedure of machine design?
- (A) Material selection
- (B) Detail drawing
- (C) Design of element
- (D) Analysis of forces
76 Detailed drawings of designed machine elements are needed by workers to machine/fabricate/assemble the machine elements. Is this statement true.
- (A) TRUE
- (B) FALSE
77 When you design a machine element you should make use of standard elements as much as possible?
- (A) TRUE
- (B) FALSE
78 A machine designer should consider the following factors among others
- (A) Workshop facilities
- (B) Selection of materials
- (C) Types of loads and stresses
- (D) All of the above
79 Compressive stress acting on the contact area between two components having no relative motion between them is known as crushing stress
- (A) TRUE
- (B) FALSE
80 At the neutral axis, bending stress is _____
- (A) Minimum
- (B) Maximum
- (C) Zero
- (D) Constant
81 What is the product of force and radius?
- (A) Twisting shear
- (B) Turning shear
- (C) Turning moment
- (D) Tilting moment
82 What is the unit of the Stress and strain
- (A) N/mm2 and mm
- (B) N and mm
- (C) N/mm and mm2
- (D) N/mm2 and No unit
83 Stress is
- (A) External force
- (B) Internal resistive force
- (C) Axial force
- (D) Radial force
84 The stress which acts in a direction perpendicular to the area is called ____________
- (A) Shear stress
- (B) Normal stress
- (C) Thermal stress
- (D) None of the mentioned
85 Which of these are types of normal stresses?
- (A) Tensile and compressive stresses
- (B) Tensile and thermal stresses
- (C) Shear and bending
- (D) Compressive and plane stresses
86 The stress induced in a body, when subjected to two equal and opposite forces which are acting tangentially across the resisting section resulting the shearing of the body across its section is called ____________
- (A) Bending stress
- (B) Compressive stress
- (C) Shear strain
- (D) Shear stress
87 Following are the basic types of stress except
- (A) Tensile stress
- (B) Compressive stress
- (C) Shear stress
- (D) Volumetric stress
88 The deformation per unit length is called
- (A) Strain
- (B) Stress
- (C) Elasticity
- (D) None of these
89 The ability of the material to deform without breaking is called
- (A) Elasticity
- (B) Plasticity
- (C) Creep
- (D) None of these
90 The stress at which extension of a material takes place more quickly as compared to increase in load, is called
- (A) No elastic zone
- (B) Plastic point
- (C) Yield point
- (D) Breaking point
91 A perfectly elastic body
- (A) Can move freely
- (B) Has perfectly smooth surface
- (C) Is not deformed by any external surface
- (D) Recovers its original size and shape when the deforming force is removed.
92 When a section is subjected to two equal and opposite forces tangentially to the section, the stress produced is known as
- (A) Tensile stress
- (B) Lateral stress
- (C) Shear stress
- (D) No stress
93 In the stress strain diagram shown in the figure, what does the letter D represent?
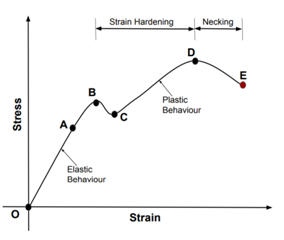
- (A) Upper yield point
- (B) Lower yield point
- (C) Ultimate limit
- (D) Braking point
94 Match the materials with the stress-strain curves in the given figure?
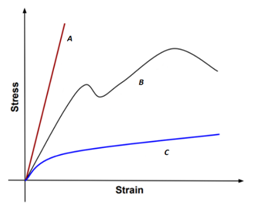
- (A) A- Cast iron, B- Plastic, C- Mild steel
- (B) A- Cast iron, B- Mild steel, C- Plastic
- (C) A- Mild steel, B- Cast iron, C- Plastic
- (D) A- Plastic, B- Cast iron, C- Mild steel
95 An example of ductile material is
- (A) Cast iron
- (B) Rubber
- (C) Glass
- (D) Mild steel
96 An example of brittle material
- (A) Cast iron
- (B) Rubber
- (C) Glass
- (D) Mild steel
97 Hooke’s law holds good up to
- (A) Yield point
- (B) Limit of proportionality
- (C) Breaking point
- (D) Elastic limit
98 Strain is defined as the ratio of
- (A) Change in volume to original volume
- (B) Change in length to original length
- (C) Change in cross-sectional are to original cross-sectional area
- (D) Any one of the above
99 It equal and opposite forces applied to a body tend to elongate it, the stress so produced is called
- (A) Internal resistance
- (B) Tensile stress
- (C) Compressive stress
- (D) Working stress
100 A thin mild steel wire is loaded by adding loads in equal increments till it breaks. The extensions noted with increasing loads will behave as under
- (A) Uniform throughout
- (B) Increase uniformly
- (C) First increase and then decrease
- (D) Increase uniformly first and then increase rapidly